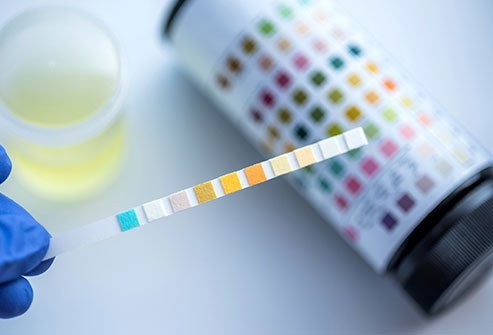
Urine analysis is a series of urine routine examinations that are used to examine and detect compounds, physical and chemical, and a microscopic study of the same. It helps doctors to identify certain diseases and conditions or monitor an already existing health condition.
The urine routine tests measure various substances present in the urine such as by-products of cellular fragments, bacteria metabolism, and cells.
Is any prior preparation required?
None, except your doctor, will recommend stopping the intake of certain medicines that could affect your test results. These protein medications include-
- Phenytoin
- Triamterene
- Chloroquine
- Levodopa
- Phenazopyridine
- Riboflavin
- Iron supplements
- Nitrofurantoin
- Phenothiazine
The different types of chemical urine routine examinations have been mentioned below-
- pH
The kidney plays a significant role in impacting and maintaining the acidic balance of the body. Any disease or condition that produces bases or acid in the body directly affects the results of urine pH. Certain crystals may develop when the urine is basic and some substances that only dissolve might precipitate to form crystals in case of acidic urine. This can be treated through changes in diet or medicine. It gradually reduces and with time, eventually eliminates.
- Bilirubin
This type of urine routine test looks for the presence of bilirubin in the urine. This is not visible in urine tests of a healthy individual. It is a by-product that is being produced by the liver from the hemoglobin of red blood cells. They are broken down and then removed from the procedure of circulation.
It results in the development of a substance, which is fluid that is excreted into the intestine to help in food digestion. This test is considered along with the detection of Urobilinogen. If required, the doctor then asks for further tests to help have a clear picture of a possible diagnosis.
- Urobilinogen
As the name suggests, this urine routine test looks out for the presence of Urobilinogen in the urine. This is present in low concentrations in most cases. It is produced in a part of the intestine from Bilirubin and some part of it is absorbed into the blood. A positive result may lead to the detection of certain liver conditions such as damage, viral hepatitis, cirrhosis due to consumption of drugs and toxic materials, or other health risks that are related to the increased damage of red blood cells.
When Urobilinogen in urine is present in low percentages or absent, this shows signs of dysfunction of the liver and it can further detect the presence of hepatic or biliary obstruction.
- Glucose
Glucose isn’t usually present in the urine and if it is present, the condition is referred to as glucosuria. It occurs either due to the presence of excessively high levels of glucose in the blood that is mostly observed in cases of people who have severe and uncontrollable levels of diabetes and in cases where there is a decrease in the renal threshold.
In such a case, the levels of glucose in the blood reach a certain amount of concentration, and then the kidneys begin to release the glucose into the urine so that blood concentrations reduce. Other conditions that can lead to glucosuria are liver diseases, hormonal disorders, pregnancy, and consumption of certain medications. When it occurs, other specific tests are recommended by doctors to have a clear understanding and identify the particular cause.
- Hemoglobin and myoglobin
This urine routine examination is conducted to understand the presence of hemoglobin in the urine. It is a protein that transports oxygen which is found inside the red blood cell. If the presence of hemoglobin is detected, it means that there is blood in the urine. A minute number of red blood cells are present in the urine but tend to result negative when a chemical test is conducted, but if there is the increased presence of hemoglobin and red blood cells they come as positive in the chemical test results.
These results are studied and detected by using micro interpreters with the help of microscopic examination. The presence of blood in the urine is not normal, but it is also not uncommon, so it does not necessarily have to lead to a negative result or be a cause for panic. It could be due to certain urinary infections too. Your doctor might be able to help you determine any cause that is leading to the presence of blood in the urine and might request for other tests to understand if there is the persistence of blood.
- Nitrite
This urine routine test determines the presence of nitrite and depends upon the basis that a lot of bacteria can transform nitrate into nitrite. Urinary tracts are meant to be free of nitrite and bacteria but if they enter the urinary tract, there are high chances of a particular infection but doesn’t always have to be alarming.
You can still have a UTI even if the test results are negative; they are considered through the procedures of microscopic examination and leukocyte esterase.
- Leukocyte esterase
This is a type of enzyme which is found in white blood cells. White blood cells are found in the urine but test negative during results. If the number of white blood cells increases to a high extent, they will be visible and come positive during results. This test is analyzed and studied through microscopic evaluation. If the result is positive, it may be an indication of infection in the urinary tract or Kidneys.
One of the most common causes for the increase in the number of white blood cells in the urine is Urinary Tract Infection. Along with white blood cells, the presence of other bacteria in the cells can also be a possibility.
- Ascorbic acid
People who consume Vitamin C tablets or multivitamins will find the presence of large amounts of ascorbic acid in urine. In this urine routine examination, a sample is requested because ascorbic acid has an impact on the accuracy of results conducted through chemical tests and causes them to turn out to be falsely low or negative.