The demand for extreme computational power has surged in recent years as artificial intelligence, machine learning, high-performance computing (HPC), 3D rendering, and gaming workloads continue to grow exponentially. Traditional CPU-based infrastructure is no longer sufficient for these compute-intensive tasks—which is why GPU as a Service has become a critical technology in 2026.
GPU as a Service allows businesses, researchers, and developers to access powerful GPUs on demand through the cloud without investing in expensive on-premise hardware. Instead of buying GPUs, you rent them—scaling up or down instantly as workloads change. This model delivers high performance, flexibility, and major cost savings.
This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know about GaaS, including benefits, use cases, pricing, providers, and the future of cloud GPUs.
What Is GPU as a Service (GaaS)?
GPU as a Service is a cloud-based model where users can deploy Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) remotely for compute-heavy workloads. Unlike CPUs, GPUs can process thousands of operations simultaneously, making them ideal for AI and compute-intensive applications.
In GaaS, cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure deliver access to powerful GPUs through virtual machines, bare-metal servers, or container-based deployments.
Why GPU Cloud Computing Matters in 2026
The GPU cloud market has exploded as organizations rush to adopt:
- Generative AI
- Large language models (LLMs)
- Autonomous driving simulations
- 4K/8K video rendering
- Scientific computing
- Crypto mining (in select regions)
Global GPU cloud spending is projected to cross $25 billion by 2027, driven primarily by AI and deep learning.
How GPU as a Service Works
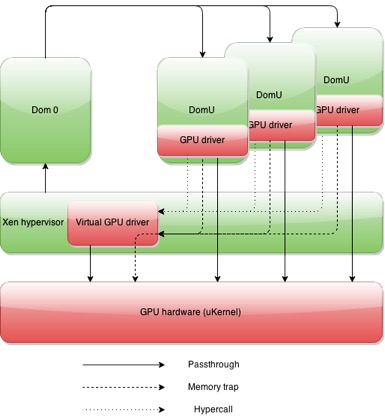
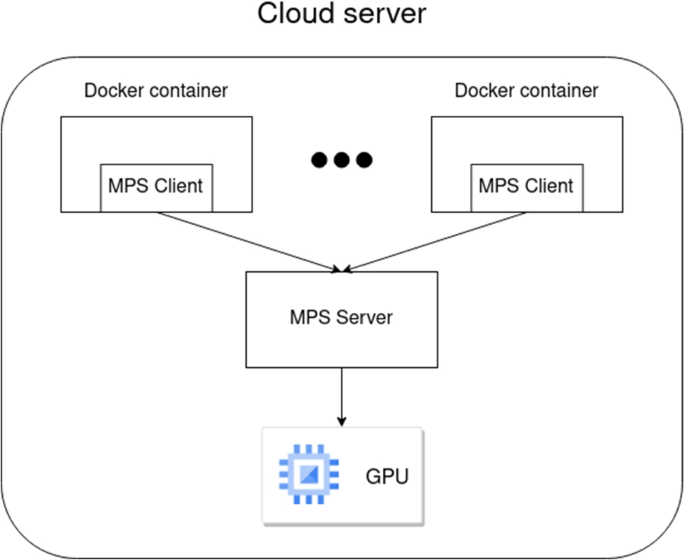
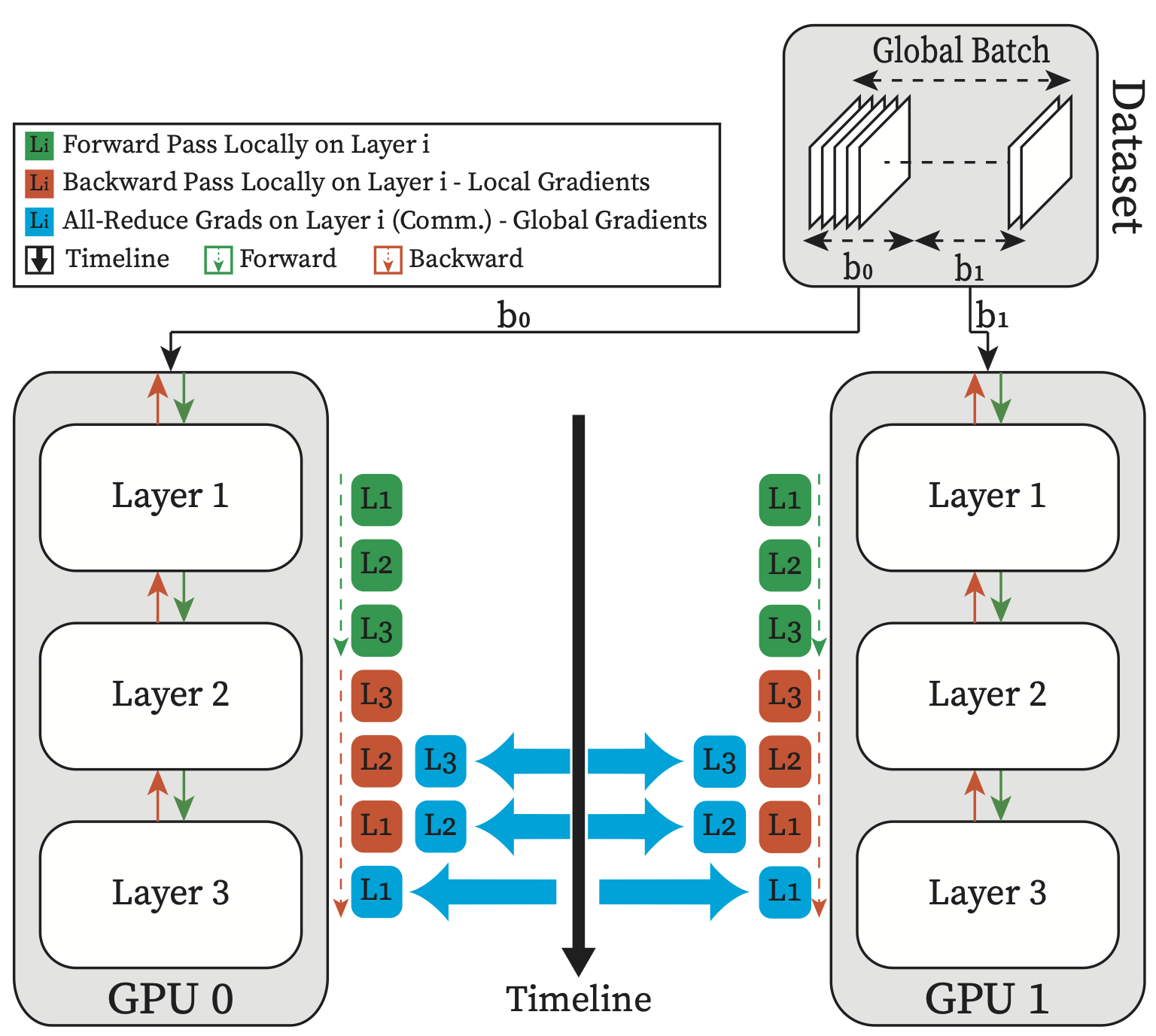
GaaS uses two common architectural approaches:
1. Virtualized GPUs
Cloud platforms divide a single physical GPU into multiple virtual GPU instances using technologies like NVIDIA vGPU.
Best for:
- Light to medium ML workloads
- Remote desktops
- Virtual workstations
2. Bare-Metal GPUs
Full access to a dedicated physical GPU.
Best for:
- Deep learning
- HPC simulations
- 3D rendering farms
- LLM training
3. GPU Clusters for Distributed Workloads
Clusters connect multiple GPUs using NVIDIA NVLink, InfiniBand, or high-bandwidth networks to scale massive AI and supercomputing tasks.
This architecture supports AI models with billions of parameters—like modern LLMs.
Benefits of GPU as a Service
1. No Hardware Investment
Buying high-end GPUs like the NVIDIA A100 or NVIDIA H100 can cost $15,000–$40,000 each. Cloud GPUs eliminate the need for upfront capital expenditure.
2. Pay-As-You-Go Flexibility
Pay only for what you use—hourly, weekly, or monthly. Ideal for startups and research projects.
3. Instant Scalability
Scale from 1 GPU to 100+ GPUs on demand for training large models or running parallel jobs.
4. Faster Performance
GPUs can deliver 10x–50x performance improvements for AI, scientific computing, and rendering compared to CPUs.
5. Global Accessibility
Deploy workloads from any region instantly using providers like:
- AWS EC2
- Google Cloud Compute Engine
- Azure GPU VMs
Top Use Cases of GPU as a Service in 2026

1. AI Training & Deep Learning
High-end GPUs accelerate:
- Neural network training
- LLM development
- Computer vision models
- Natural language processing
Models that previously required weeks on CPUs can now train in hours or days.
2. Machine Learning Pipelines
GPUs speed up:
- Data preprocessing
- Feature engineering
- Model inference
Ideal for real-time predictions and recommendation engines.
3. High-Performance Computing (HPC)
Used for:
- Weather forecasting
- Bioinformatics
- Geospatial modeling
- Chemical simulations
4. Cloud Gaming
Companies use GPU cloud servers to power low-latency gaming platforms like remote game streaming.
5. 3D Rendering & Visual Effects
Perfect for:
- Animation studios
- VFX rendering farms
- Architectural visualization
- CAD/CAM applications
6. Video Processing & Encoding
Real-time 4K/8K processing requires high GPU throughput.
7. Scientific Research
Used extensively in physics, genomics, astronomy, and engineering simulations.
GPU Types Used in Cloud Services
NVIDIA GPUs
The most widely used for cloud AI workloads:
- NVIDIA A100 – AI, HPC, LLM training
- NVIDIA H100 – World’s fastest AI GPU
- NVIDIA L40S – Inference and graphics
- NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada – Creative and rendering workloads
AMD GPUs
Great for parallel HPC and machine learning:
- AMD Instinct MI200
- AMD Instinct MI300
Which GPU Should You Choose?
- Training LLMs – H100, A100
- Inference – L40S, A10
- Rendering – RTX 6000 Ada
- HPC – MI300, A100
GaaS vs. On-Premise GPU Infrastructure
| Feature | GPU as a Service | On-Premise GPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Cost | Low | Very High |
| Maintenance | Provider-managed | In-house required |
| Scalability | Instant | Limited |
| Performance | High | High but fixed |
| Availability | Global | Local only |
Verdict:
GaaS is ideal for dynamic workloads, while on-prem GPUs suit organizations with predictable, long-term compute needs.
Best GPU Cloud Providers in 2026
1. Hyperscale Cloud Providers
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Offers P4d, P5, and G5 GPU instances
- High availability worldwide
Google Cloud
- Known for optimized AI workloads
- Offers A3 and A2 GPU VMs
Microsoft Azure
- N-series GPU VMs
- Strong enterprise security
2. Specialized GPU Cloud Providers
CoreWeave
High-performance, GPU-focused cloud; widely used for AI training.
Lambda
Great for deep learning clusters and AI research.
RunPod
Decentralized GPU compute ideal for developers.
Paperspace
Easy-to-use GPU VMs for ML, gaming, and rendering.
GPU as a Service Pricing in 2026
Prices vary based on GPU type, region, and provider.
Average On-Demand GPU Pricing
| GPU Model | Approx Cost/Hr |
|---|---|
| A100 80GB | $2.00–$4.50 |
| H100 80GB | $4.50–$12.00 |
| L40S | $1.50–$3.00 |
| RTX 6000 Ada | $1.00–$2.50 |
Pricing Models
1. On-Demand
Pay per hour—best for short training workloads.
2. Spot/Market Pricing
Significantly cheaper but not guaranteed availability.
3. Reserved Instances
Long-term commitment = Lower cost.
4. Dedicated Clusters
Used by enterprises for LLM training and supercomputing.
How to Deploy GPU Workloads on the Cloud
1. Provision a GPU Instance
Choose a VM type (A2, P4d, N-series, etc.).
2. Set Up Your AI Environment
Install:
- CUDA
- PyTorch
- TensorFlow
- NVIDIA drivers
3. Run Distributed GPU Training
Tools like:
- Horovod
- DeepSpeed
- Megatron-LM
- Ray Train
4. Optimize Performance
- Use mixed precision (FP16/FP8)
- Use fast storage (NVMe/SSD)
- Distribute datasets across nodes
- Utilize NVLink when available
Challenges & Limitations of GaaS
1. GPU Availability
High-end GPUs like H100 often sell out.
2. Cost Overruns
Unmonitored GPU workloads can become expensive.
3. Network Latency
Cloud GPU deployment is unsuitable for ultra-low-latency edge applications.
4. Data Transfer Costs
Moving large datasets can increase your bill.
Future of GPU as a Service (2026–2030)


The GPU cloud landscape is evolving rapidly:
1. Rise of AI Supercomputing
Cloud clusters with 16,000+ GPUs will become mainstream.
2. Hybrid Quantum + GPU Computing
Quantum accelerators will complement GPU compute for complex simulations.
3. Open-Source AI Models
Demand for GPUs will grow as open-source LLMs become enterprise-standard.
4. Decentralized GPU Networks
Platforms like Akash and Render will democratize GPU access worldwide.
5. Energy-Efficient GPUs
Next-gen GPUs will consume less power while delivering higher throughput.
Conclusion
GPU as a Service has transformed the way organizations approach high-performance computing in 2026. With the rise of generative AI, machine learning, HPC, rendering, and cloud gaming, GPUs have become essential for modern workloads.
GaaS solves the complexity of owning and managing physical GPUs—offering on-demand access, massive scalability, and significant cost efficiencies. Whether you’re training large AI models, running 3D rendering pipelines, or scaling scientific simulations, cloud GPUs provide unmatched performance and flexibility.
As cloud providers continue to innovate, GPU as a Service will become even more accessible, powerful, and central to the future of computing.